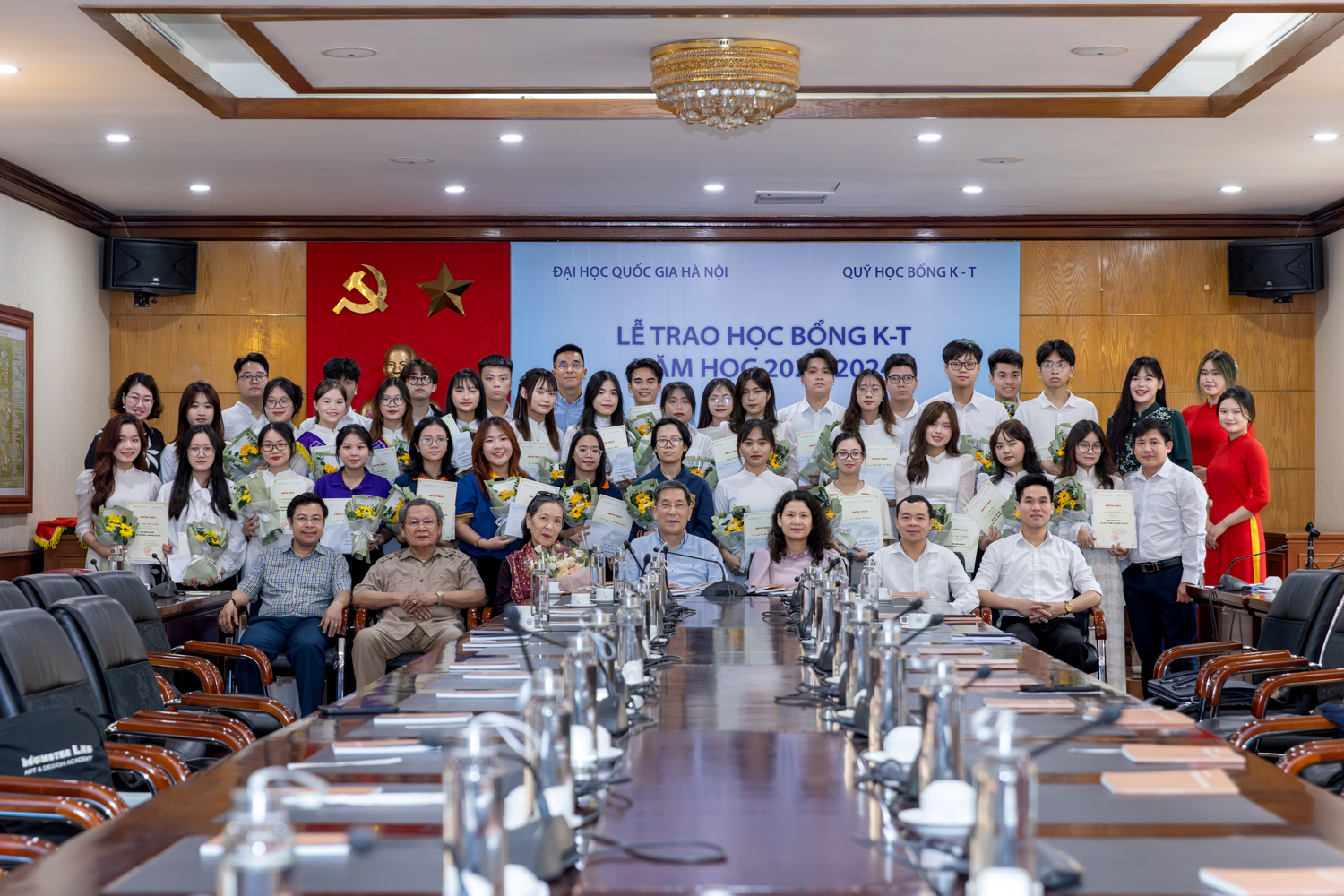
Blockade of nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway and anti-inflammatory activity of cardamomin, a chalcone analog from Alpinia conchigera
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and the signaling pathways that regulate its activity have become a focal point for intense drug discovery and development efforts. NF-κB regulates the transcription of a large number of genes, particularly those involved in immune, inflammatory, and antiapoptotic responses. In our search for NF-κB inhibitors from natural resources, we identified cardamomin, 2′,4′-dihydroxy-6′-methoxychalcone, as an inhibitor of NF-κB activation from Alpinia conchigera Griff (Zingiberaceae). In present study, we demonstrated the effect of cardamomin on NF-κB activation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and LPS-induced mortality. This compound significantly inhibited the induced expression of NF-κB reporter gene by LPS or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in a dose-dependent manner. LPS-induced production of TNF-α and NO as well as expression of inducible nitric-oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 was significantly suppressed by the treatment of cardamomin in RAW264.7 cells. Also, cardamomin inhibited not only LPS-induced degradation and phosphorylation of inhibitor κBα (IκBα) but also activation of inhibitor κB (IκB) kinases and nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Further analyses revealed that cardamomin did not directly inhibit IκB kinases, but it significantly suppressed LPS-induced activation of Akt. Moreover, cardamomin suppressed transcriptional activity and phosphorylation of Ser536 of RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB. However, this compound did not inhibit LPS-induced activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH 2-terminal kinase, but significantly impaired activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. We also demonstrated that pretreatment of cardamomin rescued C57BL/6 mice from LPS-induced mortality in conjunction with decreased serum level of TNF-α. Together, cardamomin could be valuable candidate for the intervention of NF-κB-dependent pathological condition such as inflammation. Copyright © 2006 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
| Lee J.-H., Haeng S.J., Phan M.G., Jin X., Lee S., Phan T.S., Lee D., Hong Y.-S., Lee K., Jung J.L.
|
 684.pdf 684.pdf
 Gửi cho bạn bè Gửi cho bạn bè
|
|
Từ khóa :
2',4' dihydroxy 6' methoxychalcone; antiinflammatory agent; chalcone derivative; cyclooxygenase 2; I kappa B; immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein; inducible nitric oxide synthase; lipopolysaccharide; mitogen activated protein kinase; mitogen activated protein kinase p38; nitric oxide; protein kinase B; serine; stress activated protein kinase; tumor necrosis factor alpha; unclassified drug; Alpinia; Alpinia conchigera; animal cell; animal experiment; antiinflammatory activity; article; cell death; controlled study; cytokine production; drug effect; drug efficacy; drug mechanism; enzyme inactivation; gene expression regulation; human; human cell; inhibition kinetics; male; mouse; nonhuman; pharmacogenetics; priority journal; protein phosphorylation; reporter gene; signal transduction; transcription regulation; Alpinia; Animals; Anti-Inflammatory Agents; Blotting, Western; Cell Survival; Chalcones; Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors; Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay; Enzyme Inhibitors; Humans; I-kappa B Proteins; Lipopolysaccharides; Luciferases; Macrophages; Mice; Mice, Inbred C57BL; NF-kappa B; Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II; Oncogene Protein p65(gag-jun); Phosphorylation; Plasmids; Signal Transduction; Trans-Activation (Genetics); Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
|

 684.pdf
684.pdf
 Gửi cho bạn bè
Gửi cho bạn bè









